 | Banjo,
 | African names “banjar”, “banjil”, “banza”,
“bangoe”, “bangie”, “banshaw”. |
 | 1620 Richard Jobson while exploring the Gambra River in Africa in 1620 he recorded an
instrument “...made of a great gourd and a neck, thereunto was fastened
strings.” |
|
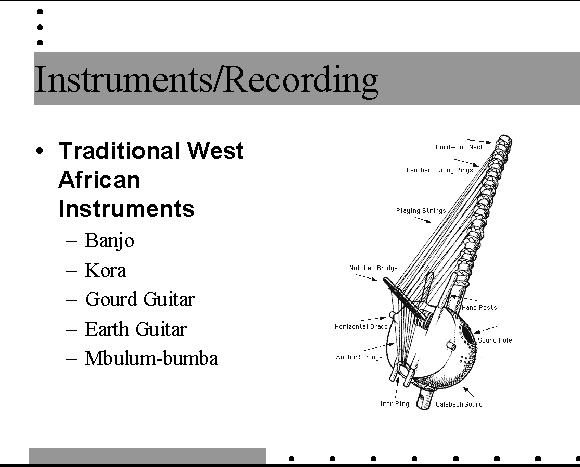
 | Mandinka kora
 | Looks like a harp, but its playing style is closer to flamenco guitar. |
 | The first known reference to the kora comes from 1799 Mungo Park Travels in Interior
Districts of Africa. He describes it as “a large harp with 18 strings”. |
 | The kora’s body is made from a calabash gourd cut in half and partially covered
with cow skin. Traditionally, there are twenty-one playing strings plucked by the thumb
and forefinger of each hand. |
 | The remaining fingers grip the two vertical hand posts. For strings, players use fishing
line which provides a brillant tone and is easily obtained at the local market. Twenty-one
anchor strings attach the playing strings to an iron ring bored through the base of the
kora’s hardwood neck. |
 | The player tunes the kora by moving the leather rings to achieve the appropriate tension
on each string. Kora players use a variety of tunings. |
|
 | Audio: "Alla L'aa ke" played by Alhaji Bai Konte Traditional musical pattern,
played to check the kora's tuning
 | Gourd guitar - Gonje or Gouje |
 | Earth Guitar - Hole in the ground with a resonating membrane.Mbulum-bumba, single string
bow harp from - Called Berimbau |
|

![]()